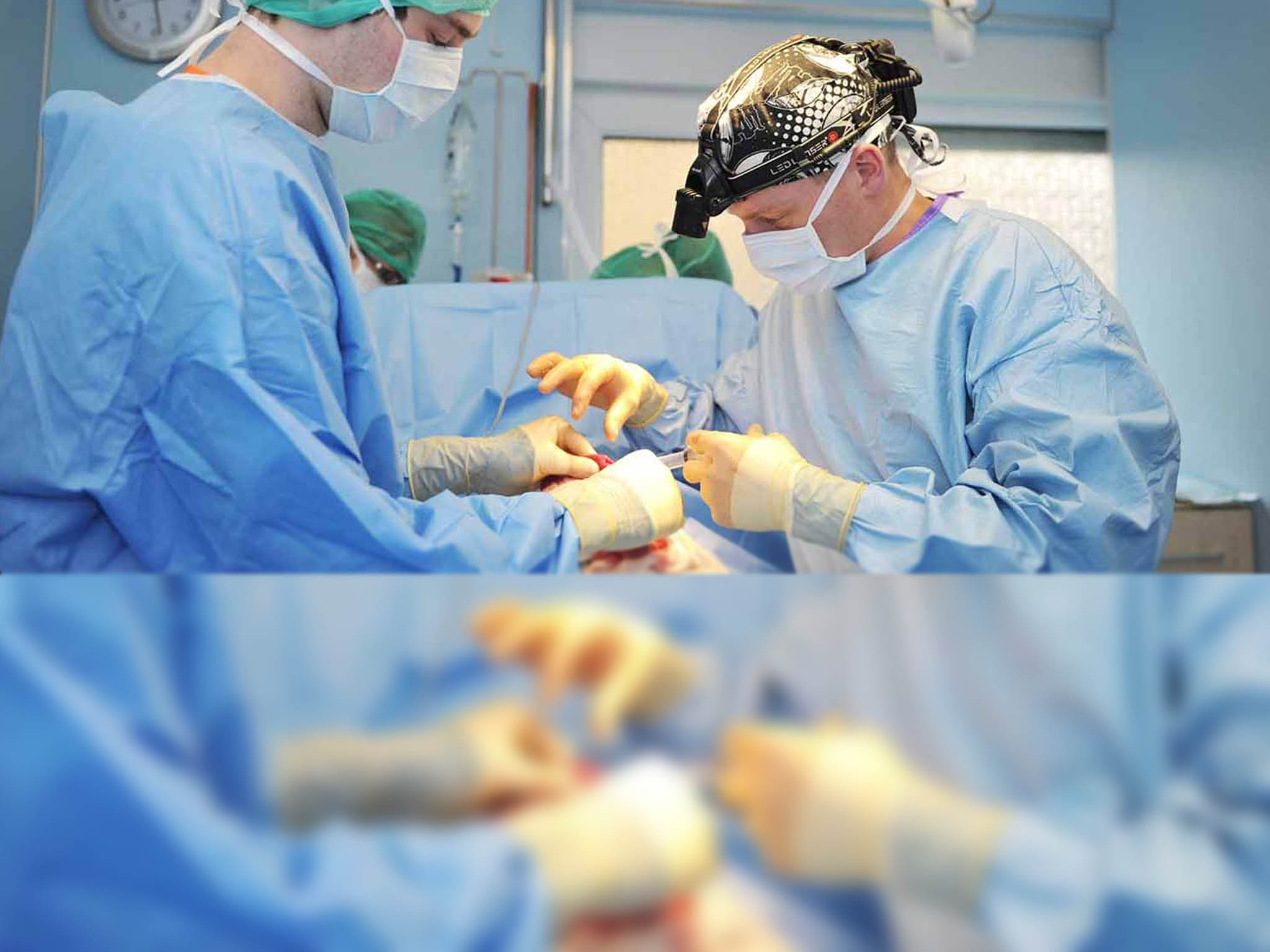
Abdomen Surgery
Abdominal surgery refers to any surgical operation on abdominal organs, including the stomach, gallbladder, small intestine, large intestine, appendix, liver, pancreas, spleen, esophagus and appendix. The procedures may be performed for a variety of reasons, including infection, obstruction, tumors or inflammatory bowel disease.
There are many types of abdominal surgery. A few of the more common ones include inguinal hernia surgery, abdominal exploration surgery, appendectomy or surgery for inflammatory bowel disease, which may involve removing all or part of the small or large intestine. These specific operations and the conditions associated with them are discussed in greater detail in the Related Conditions section.
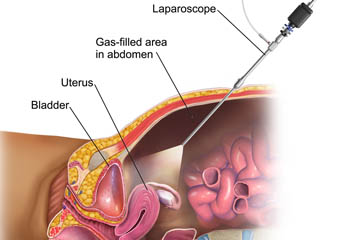
Laparoscopic surgeries make use of tubes that are inserted into tiny incisions made on the patient's body. The tubes are attached to a video camera that gives the surgeon a view of the abdominal interior as a guide during the surgery. Surgical instruments are also designed to work with the said tubes, completely eliminating the need for making large incisions. As a result, patients recover from the procedure faster and also experience minimal blood loss and minimal scarring. They also greatly reduce the risk of infection. This minimally invasive approach to abdominal surgery is becoming more and more in demand these days as laparoscopic technology continues to improve.
How Does the Procedure Work?
There are a number of abdominal surgical procedures, and each is performed using different techniques.
Caesarean section - Dubbed as a C-section, this is an abdominal procedure used for childbirth purposes, i.e. delivery of full-term babies, although in complicated cases, it may also entail the removal of a dead fetus. This procedure requires making a large incision through the abdominal of the expectant mother in a method called laparotomy, and also through the uterus in a method called hysterotomy.
Inguinal hernia surgery - This is an abdominal procedure intended for the repair of an inguinal hernia. It involves creating an incision near the location of the hernia to remove the sac and later on, to push the intestine back into the abdomen. This is typically performed using laparoscopic techniques.
Exploratory laparotomy - This is a diagnostic surgery that aims to determine the source of bleeding or trauma that affects the abdominal organs and causes distressing symptoms to the patient. This involves opening the abdominal cavity to directly examine the contents of the abdominal cavity. If the situation allows, the same procedure is used to repair or remove the problem.
Cholecystectomy - This is an abdominal surgery intended to remove the gallbladder. This is the most common type of laparoscopic abdominal surgery at present.
Appendectomy - This abdominal surgery is intended for people suffering from appendicitis, or the inflammation of the appendix. This is the definitive course of treatment for appendicitis and involves removing the appendix altogether. In some cases, the appendix may rupture, making an appendectomy an urgent procedure to avoid complications.